
이번에는 다양한 방법으로 bean객체에 값을 주입하고 호출해 볼예정입니다.
우선 다음과 같은 구조의 패키지를 구성하겠습니다.
Score.java
package com.test01;
public class Score {
private String name;
private int kor;
private int eng;
private int math;
private int sum;
private double avg;
private String grade;
public Score() {
}
public Score(String name, int kor, int eng, int math) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
}
public Score(String name, int kor, int eng, int math, int sum, double avg, String grade) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
this.sum = sum;
this.avg = avg;
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getKor() {
return kor;
}
public void setKor(int kor) {
this.kor = kor;
}
public int getEng() {
return eng;
}
public void setEng(int eng) {
this.eng = eng;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getSum() {
return sum;
}
public void setSum(int sum) {
this.sum = sum;
}
public double getAvg() {
return avg;
}
public void setAvg(double avg) {
this.avg = avg;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Score [name=" + name + ", kor=" + kor + ", eng=" + eng + ", math=" + math + ", sum=" + sum + ", avg="
+ avg + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
}MyClass.java
package com.test01;
public class MyClass {
public MyClass() {
System.out.println("MyClass Constructor!!!");
}
public void prn() {
System.out.println("MyClass.prn(); !!!!!");
}
}BeanTest.java
package com.test01;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class BeanTest {
private MyClass myclass;
// 0.
public BeanTest() {
System.out.println("BeanTest 기본생성자!");
}
// 1.
public BeanTest(MyClass myclass) {
this.myclass = myclass;
System.out.println("BeanTest(MyClass) 생성자!");
}
public BeanTest(Date date) {
System.out.println("BeanTest(Date) 생성자!");
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
}
// 2.
public void setMyclass(MyClass myclass) {
this.myclass = myclass;
System.out.println("setMyclass(MyClass myclass) 호출 !!");
}
// 3.
public void setDate(Date date) {
System.out.println("setDate(Date date) 호출!!");
System.out.println("end : " + date.toLocaleString());
}
// 4.
public void setNumber(int num) {
System.out.println("setNumber(int num) 호출 : " + num);
}
// 5.
public void setArray(String[] arr) {
System.out.println("setArray(String[] arr) 호출");
for(String s : arr) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
// 6.
public void setList(List<String> list) {
System.out.println("setList(List<String> list) 호출!");
for(String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
// 7.
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
System.out.println("setSet(Set<String> set) 호출!");
for(String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
// 8.
public void setMap(Map<Integer, String> map) {
System.out.println("Map<Integer, String> map 호출!");
// Entry 써서 k : v 형태로 출력하자.
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
// 9.
public void setScore(List<Score> list) {
System.out.println("setScore(List<Score> list) 호출!");
for(Score sc : list) {
System.out.println(sc);
}
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="today" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- Date today = new Date(); -->
<bean id="end" class="java.util.Date">
<!-- year에는 1900을 더한 값이 나오며 month는 0부터 시작 -->
<constructor-arg name="year" value="121" />
<constructor-arg name="month" value="6" />
<constructor-arg name="date" value="14" />
</bean>
<bean id="myclass" class="com.test01.MyClass"></bean>
<bean id="beanTest" class="com.test01.BeanTest">
<!-- 0. 아무 내용도 없으면 기본생성자 -->
<!-- 1. param 1개짜리 생성자 -->
<!-- <constructor-arg name="myclass" ref="myclass" /> -->
<constructor-arg ref="today" />
<!-- 2. setMyclass 호출 -->
<property name="myclass" ref="myclass" />
<!-- 3. setDate(Date date) 호출 -->
<property name="date" ref="end" />
<!-- 4. setNumber(int num) 호출 -->
<!-- <property name="number" value="28" /> -->
<property name="number">
<!-- short로 선언시 묵시적 형변환 -->
<value type="short">
28
</value>
</property>
<!-- 5. setArray(String[] arr) 호출 -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>라붐</value>
<value>상상</value>
<value>더하기</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 6. setList(List<String> list) 호출 -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>봄</value>
<value>여름</value>
<value>가을</value>
<value>겨울</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 7. setSet(Set<String> set) 호출 -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>1</value>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>3</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- 8. Map<Integer, String> map 호출 -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>1</value></key>
<value>봄</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>2</value></key>
<value>여름</value>
</entry>
<entry key="3" value="가을"></entry>
<entry key="4" value="겨울" />
</map>
</property>
<!-- 9. setScore(List<Score> list) 호출 -->
<property name="score">
<list>
<bean class="com.test01.Score">
<property name="name" value="홍길동" />
<property name="kor" value="100" />
<property name="eng" value="100" />
<property name="math" value="100" />
</bean>
<ref bean="han" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="han" class="com.test01.Score">
<constructor-arg value="한효주" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
</bean>
</beans>MTest.java
package com.test01;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
public class MTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/test01/applicationContext.xml");
Date today = (Date) factory.getBean("today");
System.out.println(today.toLocaleString());
MyClass myclass = (MyClass) factory.getBean("myclass");
myclass.prn();
}
}실행결과
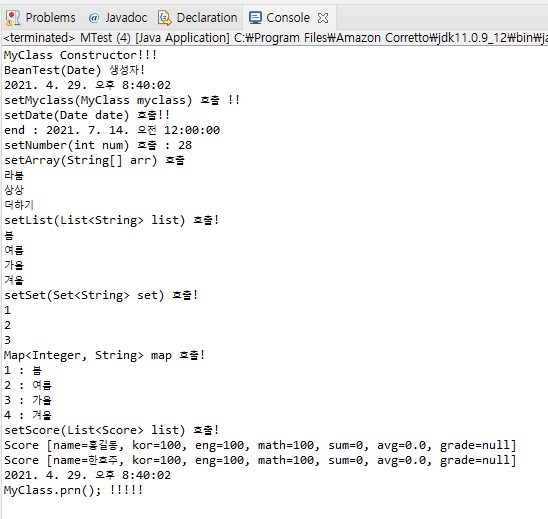
코드가 매우 복잡하죠?
Score, MyClass, MTest말고 BeanTest와 applicationContext에 번호를 달아놨으니 번호 순서대로 따라가면서 보도록 하죠!
우선 그전에 번호는 없지만
Date today = (Date) factory.getBean("today");
System.out.println(today.toLocaleString());MTest의 해당 코드로 날짜를 출력할수 있습니다. factory 메소드를 통해 today객체가 호출되려면 xml에 today객체가 생성이 되어있어야 하며 toLocaleString()는 날짜의 형태를 바꾸기 위해 사용하였습니다.
<bean id="today" class="java.util.Date"></bean>임의로 만든 클래스만 객체선언을 할수 있는게 아니라 자바에서 제공하는 클래스로도 객체를 만들수 있습니다.
<!-- Date today = new Date(); -->위의 코드는 자바에서 이와 같이 객체를 생성할 때의 코드와 동일합니다.
<bean id="end" class="java.util.Date">
<!-- year에는 1900을 더한 값이 나오며 month는 0부터 시작 -->
<constructor-arg name="year" value="121" />
<constructor-arg name="month" value="6" />
<constructor-arg name="date" value="14" />
</bean>또한 year, month, date등의 값을 넣어줄수 있는데요.
학원의 수료일인 2021년 7월14일을 출력하기 위해서는 year에 121, month에 6을 입력해주어야 합니다.
year에는 1900을 더한값이 출력되며 month는 0부터 시작하기 때문에 6을 입력해야 7이 출력이 됩니다.
<bean id="myclass" class="com.test01.MyClass"></bean>와 같이 객체를 생성했습니다. bean태그 사이에 아무 내용이 없으면 factory메서드를 이용해 호출 될때 기본생성자가 호출됩니다.

<bean id="beanTest" class="com.test01.BeanTest">
</bean>이제부터는 이 안에 여러가지 속성을 넣볼 예정입니다.
이후 적는 <construct-arg>태그와 <property>태그는 BeanTest클래스 타입의 객체 beanTest객체를 만드는 <bean>안에 있다고 생각해주세요!
1. param 1개짜리 생성자
public BeanTest(MyClass myclass) {
this.myclass = myclass;
System.out.println("BeanTest(MyClass) 생성자!");
}
public BeanTest(Date date) {
System.out.println("BeanTest(Date) 생성자!");
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
}<constructor-arg name="myclass" ref="myclass" />
<constructor-arg ref="today" />위 두개의 형태에 따른 생성자를 호출했다고 가정하면
두개의 생성자중 타입에 맞게 호출이 됩니다.
첫번째 myclass라는 변수명으로 MyClass타입의 객체가 있기때문에
BeanTest(MyClass) 생성자!
라는 결과가 출력 될 것입니다.
(편의상 출력 결과는 파란색으로 작성하겠습니다)
또한 두번째 today는 date타입으로 선언이 되어있기 때문에
BeanTest(Date) 생성자!
가 출력이 됩니다.
하지만 위의 전체 코드에서는 첫번째 줄이 주석처리 되어있기때문에 아래의 값만 실행됩니다.

2. setMyclass 호출
public void setMyclass(MyClass myclass) {
this.myclass = myclass;
System.out.println("setMyclass(MyClass myclass) 호출 !!");
}<property name="myclass" ref="myclass" />해당 코드는 세터에 값을 주입하게 됩니다.
myclass에서 첫번째 글자만 대문자로 바꾼 setMyclass 메서드를 찾아서 호출하게 됩니다.
해당 메서드를 찾겠네요.
getMyclass대신에 this.myclass=myclass를 이용했습니다!
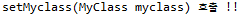
3. setDate(Date date) 호출
public void setDate(Date date) {
System.out.println("setDate(Date date) 호출!!");
System.out.println("end : " + date.toLocaleString());
}<property name="date" ref="end" />해당 메서드를 호출하게 되는데 아까 만들어 놓은 end객체를 참조합니다.
날짜를 출력하지만 지정해준 날짜가 출력이 되곘죠?
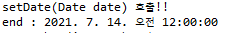
4. setNumber(int num) 호출
public void setNumber(int num) {
System.out.println("setNumber(int num) 호출 : " + num);
}<property name="number">
<!-- short로 선언시 묵시적 형변환 -->
<value type="short">
28
</value>
</property><property name="number" value="28" />위 둘중 아무코드나 작성해도 setNumber(int num)형태의 메서드(세터)가 호출됩니다.
다만 int로 선언되어있는 파라미터1개짜리 생성자가 호출되어야 하지만 short 타입으로 아규먼트를 주게 되면 묵시적 형변환 되어 에러 발생없이 호출이 가능합니다.
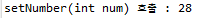
5. setArray(String[] arr) 호출
public void setArray(String[] arr) {
System.out.println("setArray(String[] arr) 호출");
for(String s : arr) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}<property name="array">
<array>
<value>라붐</value>
<value>상상</value>
<value>더하기</value>
</array>
</property>배열은 어떻게 호출할까요??
<array>태그를 작성한후 그 안에 <value>태그를 넣어 값을 주입하면됩니다.
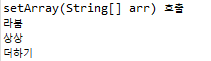
6. setList(List<String> list) 호출
public void setList(List<String> list) {
System.out.println("setList(List<String> list) 호출!");
for(String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}<property name="list">
<list>
<value>봄</value>
<value>여름</value>
<value>가을</value>
<value>겨울</value>
</list>
</property>list타입을 호출하기 위해서는 <list>태그 안에 값을 작성하면 됩니다.
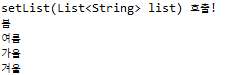
7. setSet(Set<String> set) 호출
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
System.out.println("setSet(Set<String> set) 호출!");
for(String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}<property name="set">
<set>
<value>1</value>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>3</value>
</set>
</property>set타입도 마찬가지로 <set>태그 안에 값을 넣어줍니다!
대신 set 타입의 특성에 맞게 중복된 결과는 출력되지 않습니다
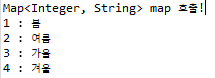
8. Map<Integer, String> map 호출
public void setMap(Map<Integer, String> map) {
System.out.println("Map<Integer, String> map 호출!");
// Entry 써서 k : v 형태로 출력하자.
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key>
<value>1</value>
</key>
<value>봄</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key>
<value>2</value>
</key>
<value>여름</value>
</entry>
<entry key="3" value="가을"></entry>
<entry key="4" value="겨울" />
</map>
</property>Map의 경우도 <map>태그 안에 넣어주면 되는데 Entry를 사용했을 경우에는 <entry>태그도 작성하면 됩니다!
Map의 특성인 Key, Value의 형태에 맞게 Key값은<key>태그를 통해 Value값은 <value>태그를 통해 주입합니다.
9. setScore(List<Score> list) 호출
public void setScore(List<Score> list) {
System.out.println("setScore(List<Score> list) 호출!");
for(Score sc : list) {
System.out.println(sc);
}
}<property name="score">
<list>
<bean class="com.test01.Score">
<property name="name" value="홍길동" />
<property name="kor" value="100" />
<property name="eng" value="100" />
<property name="math" value="100" />
</bean>
<ref bean="han" />
</list>
</property><bean id="han" class="com.test01.Score">
<constructor-arg value="한효주" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
<constructor-arg value="100" />
</bean>list를 호출할때 제네릭이 객체타입일 경우 하나씩 값을 넣어주는 방법도 있지만 만들어진 객체를 참조하는 방법도 있습니다.
set이랑 map도 마찬가지겠죠?
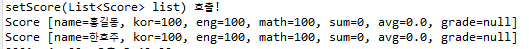
'Java 관련 > Spring Legecy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체_10) - MessageSourceAware (0) | 2022.03.20 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체_10) - autowire (0) | 2022.03.19 |
| [Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체 생성_08) - <bean>태그 속성 (0) | 2022.03.17 |
| [Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체 생성_07) - schema/c(c:), schema/p(p:) (0) | 2022.03.16 |
| [Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체 생성_06) - 객체 참조(ref) (0) | 2022.03.15 |
![[Spring] DI / IoC (Bean 객체_09) - 호출](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FcXbIz1%2Fbtrne04Lh35%2F8wLFFjD518VbvnzkbVfnGK%2Fimg.png)